- August 20, 2021
- 0 Comments
- In Existing Building Performance High-Performance Construction
- By Steven Winter Associates
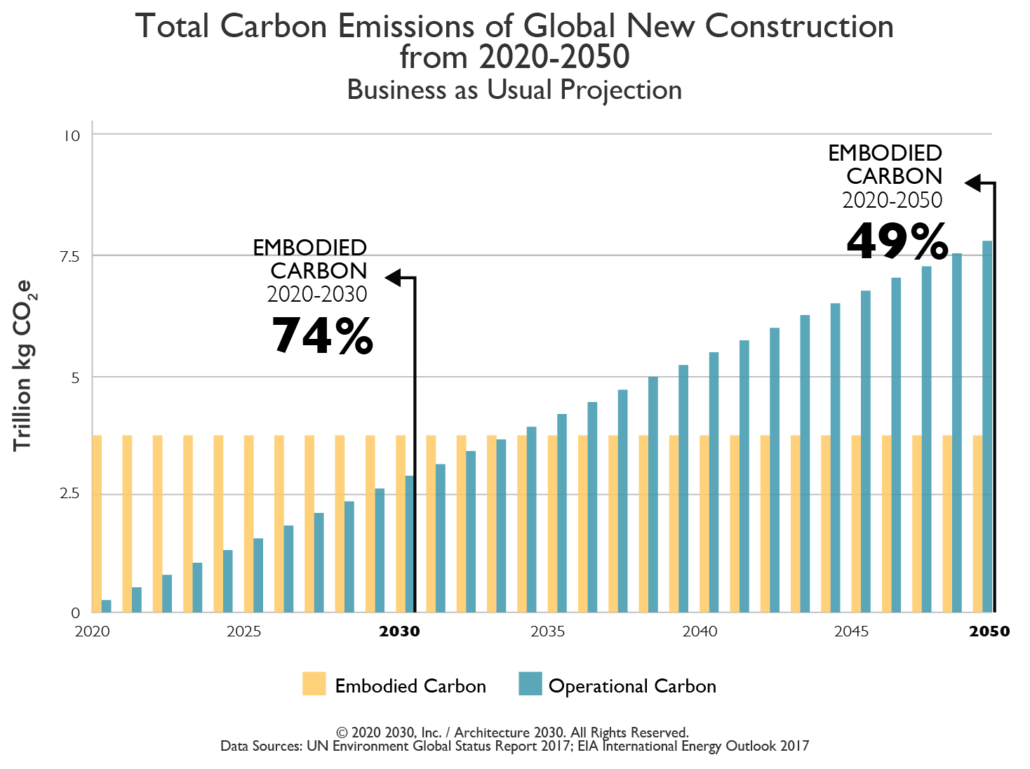 To meet the goals of the Paris Climate Agreement, we must make decisions that will result in the greatest near-term carbon savings. This means taking into account both embodied carbon—those upfront emissions associated with the extraction, manufacture, transportation, and assembly of building materials—as well as the carbon that’s emitted over the course of the building’s operational phase.
To meet the goals of the Paris Climate Agreement, we must make decisions that will result in the greatest near-term carbon savings. This means taking into account both embodied carbon—those upfront emissions associated with the extraction, manufacture, transportation, and assembly of building materials—as well as the carbon that’s emitted over the course of the building’s operational phase.
We can build a high-performance building with very low operational emissions, but if its embodied emissions are so high that even if it’s a net-zero energy building (meaning it has net-zero operational energy consumption) it would take decades for the building to reach net-zero carbon (meaning it has net zero whole-building lifetime carbon emissions), we’re not actually helping to solve the critical issue of near-term carbon.