 Now that HUD has adopted the 2009 edition of the ICC A117.1 Standard and the 2009, 2012, 2015, and 2018 editions of the IBC as additional safe harbors that can be used to demonstrate compliance with the design and construction requirements of the FHA, what changes? What do designers need to know before moving forward with selecting their chosen safe harbor? Here are a few of the most common questions that our Accessibility Team has been asked about the use of the new safe harbors since they became effective on March 8, 2021:
Now that HUD has adopted the 2009 edition of the ICC A117.1 Standard and the 2009, 2012, 2015, and 2018 editions of the IBC as additional safe harbors that can be used to demonstrate compliance with the design and construction requirements of the FHA, what changes? What do designers need to know before moving forward with selecting their chosen safe harbor? Here are a few of the most common questions that our Accessibility Team has been asked about the use of the new safe harbors since they became effective on March 8, 2021:
The New FHA Safe Harbors: FAQs
Designing for Inclusion with Victoria Lanteigne
Disability inclusion in the built environment is extremely important. But, it shouldn’t end there. How do we ensure that we are being truly inclusive of all types of people, taking into account a wider diversity of backgrounds, orientations, and abilities? The answer is Universal Design.
On this episode of Building’s + Beyond, Robb chats with former SWA employee and Universal Design expert, Victoria Lanteigne. Victoria has devoted her career to the advancement of Universal Design, educating herself and others on the concept and its limitless applications. In her interview, she discusses trends, tactics, and examples from the field, and challenges practitioners to re-think their definition of the word, design.
Accessibility Tech Notes: Sliding Doors at Dwelling Units
Private outdoor space is a desirable amenity for apartment dwellers, especially as COVID-19 restrictions have led to more time spent at home. Balconies and terraces accessed directly from multifamily residential dwelling units are increasingly popular with many of our clients, a trend we expect to see continue in the coming years. For designers looking to incorporate this feature, it is important to note that secondary exterior doors from dwelling units have specific accessibility considerations.
One of the most common problem areas that our accessibility consultants see in multifamily housing units are noncompliant secondary exterior sliding doors. The Fair Housing Act (FHA), as well as most building codes, strictly regulate these doors, from clear width and thresholds to door hardware at certain unit types. Our consultants highly recommend that swing doors are used in lieu of sliding doors at secondary exterior locations; however, if a sliding door is preferred, it is vital to consider the following requirements, among others:
Trends in Healthcare: Charging Stations
“Trends in Healthcare” is a recurring series that focuses on exciting new designs and technologies we’re seeing in healthcare projects and provides best practices on how to ensure that these latest trends are accessible to persons with disabilities. We build on the wealth of knowledge we gain from working with healthcare design teams, construction crews, and practitioners to provide practical solutions for achieving accessible healthcare environments.
Anyone who has ever had to take a trip to the hospital knows how much time is often spent in the waiting room. As a result, our experience in that space can shape our perception of the entire visit. In fact, studies have shown that a visitor’s impression of the waiting room itself contributes significantly to the likelihood of a return visit.[1] The length of wait times can vary – from a relatively short wait for a screening, to an average of 40 minutes in emergency departments, to the better part of a day if you are waiting for a family member to receive treatment.[2] As healthcare providers strive to remove pain points within the patient experience, they are turning to a number of design strategies to help create a more pleasant waiting room experience. One of these strategies is to ensure that patients and visitors have access to electrical outlets.
Accessibility Tech Notes: Automatic Doors
 As the country continues to confront the realities of the COVID-19 pandemic, the way we navigate spaces is changing. One of these changes is the way we interact with common use objects that traditionally require hand-operation, like doors. While automatic doors have always been a good option for providing greater access to people with disabilities, hygiene concerns associated with the spread of disease have presented another argument for their use. The rise of touchless technology as a result of this pandemic will increase the use of automatic doors not just for accessibility or convenience, but for public health as well. For anyone considering incorporating automatic doors into their designs, either for new construction or as a retrofit, here are some important things to consider:
As the country continues to confront the realities of the COVID-19 pandemic, the way we navigate spaces is changing. One of these changes is the way we interact with common use objects that traditionally require hand-operation, like doors. While automatic doors have always been a good option for providing greater access to people with disabilities, hygiene concerns associated with the spread of disease have presented another argument for their use. The rise of touchless technology as a result of this pandemic will increase the use of automatic doors not just for accessibility or convenience, but for public health as well. For anyone considering incorporating automatic doors into their designs, either for new construction or as a retrofit, here are some important things to consider:
Accessibility Tech Notes: Door Surface
The 2010 ADA Standards and the A117.1 Standard for Accessible and Usable Buildings and Facilities require the bottom 10 inches on the push side of a door to be smooth and free from any obstructions for the full width of the door. While there are some exceptions (e.g., sliding doors or tempered glass doors without stiles), this requirement applies at the following locations:
- 2010 ADA Standards:
- Public and Common Use Areas: All doors along the accessible route
- Accessible Dwelling Units: The primary entry door and all doors within the unit intended for user passage
- A117.1 Standard:
- Public and Common Use Areas: All doors along the accessible route
- Type B Dwelling Units: The primary entry door
- Type A and Accessible Dwelling Units: The primary entry door and all doors within the unit intended for user passage
 The door surface provision is intended to ensure the safety of people with disabilities who require the use of a wheelchair, walker, cane, or other mobility aid. It is common to utilize the toe of the wheelchair or leading edge of another mobility device to push open a door while moving through it. The smooth surface allows the footrest of a wheelchair or other mobility device that comes into contact with the door to slide across the door easily without catching.
The door surface provision is intended to ensure the safety of people with disabilities who require the use of a wheelchair, walker, cane, or other mobility aid. It is common to utilize the toe of the wheelchair or leading edge of another mobility device to push open a door while moving through it. The smooth surface allows the footrest of a wheelchair or other mobility device that comes into contact with the door to slide across the door easily without catching.
5 New Year’s Resolutions for a High-Performance Year
We took some common New Year resolutions and put our SWA spin on them. This year, make resolutions to improve the built environment in 2020!
- Go on a (Carbon) Diet – diets are difficult, but as with all things, moderation is key. Reducing operational carbon use with super-efficient buildings is only part of the equation. We also need to understand the full Life Cycle of carbon use including building materials and products. Fortunately tools such as EC3 are making these analyses easier to understand; and products, including lower carbon insulation options and lower carbon concrete, are becoming readily available.
- Quit Smoking – enforcing no smoking policies is one of the best strategies to improve the health of all building occupants. If you do allow smoking, make sure you develop a good fresh air strategy and compartmentalize your units with a good air barrier. And check out more of our strategies for healthy indoor environments.
- Save More Money – lighting provides a significant area for savings. Sure, LEDs are great, but efficient design also means considering lighting power density (LPD). High efficiency fixtures placed in high concentrations still use a lot of energy and can result in over-lit spaces, which drive up upfront and operating costs. Lower your bills and the harsh glare with a smart lighting design.
- Travel More – seek out hotels and restaurants that people of all abilities can navigate with ease. Access Earth is an app that tracks the accessibility of public spaces worldwide to help take the guesswork out of accessible accommodations in new locations.
- Learn a New Skill or Hobby – looking to expand your horizons? Check out SWA Careers and join our team of change-makers to help develop and implement innovative solutions to improve the built environment.
Tech Notes: Accessible Parking in Precast Garages
 When designing accessible parking spaces, it is important to remember that the slope of the ground surface for the entire parking space and adjacent access aisle must not exceed 2% in any direction. We frequently see noncompliant slopes at accessible spaces, especially when the ground surface is asphalt or permeable pavers. The slope along the perimeter of spaces at curbs or gutters is frequently more than 2% at up to 5%, which requires careful detailing and planning on the part of the architect, civil engineer, and on site contractors to ensure that a compliant slope is achieved at the accessible parking spaces. At parking structures and precast garage systems, we have found that important details and coordination needed to achieve compliant ground surface slopes are often overlooked.
When designing accessible parking spaces, it is important to remember that the slope of the ground surface for the entire parking space and adjacent access aisle must not exceed 2% in any direction. We frequently see noncompliant slopes at accessible spaces, especially when the ground surface is asphalt or permeable pavers. The slope along the perimeter of spaces at curbs or gutters is frequently more than 2% at up to 5%, which requires careful detailing and planning on the part of the architect, civil engineer, and on site contractors to ensure that a compliant slope is achieved at the accessible parking spaces. At parking structures and precast garage systems, we have found that important details and coordination needed to achieve compliant ground surface slopes are often overlooked.
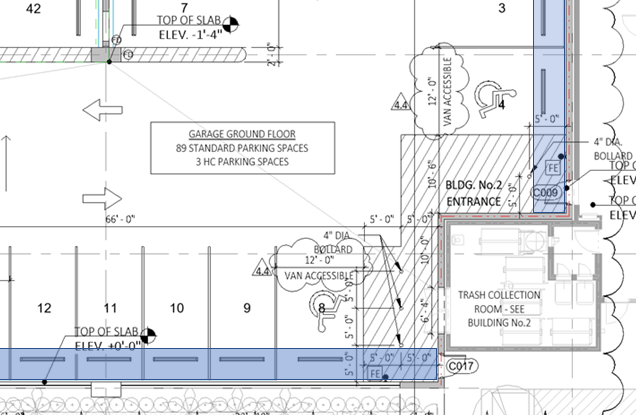
Ground surface slopes at walls or parapets often exceed 2%, (blue highlight) resulting in noncompliant slopes at the heads of accessible parking spaces.
In parking structures, it is common for an area along the perimeter of the slab (adjacent to walls or parapets) to slope in excess of 2% for drainage purposes. In some cases, this slope is embedded into the precast system. As a result, accessible parking spaces must be located away from the sloped edges during the initial design phase.
In other cases, noncompliance results from the application of a cast in place (CIP) wash applied to the top of the precast slab. In the detail shown below, note the slope condition at the CIP topping. The wash is often indicated only in section details on the precast drawing set, making it easy to miss if designers are not specifically looking for how these details affect accessible parking spaces. The entire project team involved in the design and/or construction of the garage must be made aware of where accessible parking spaces are located and understand the specific slope requirements to ensure that details are properly coordinated.
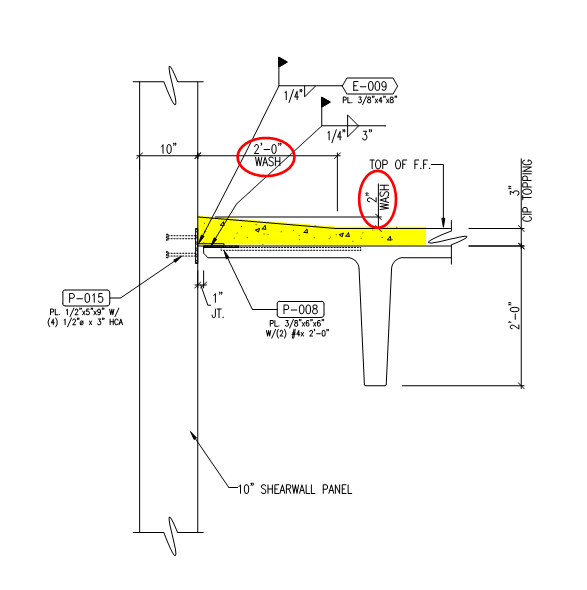
The cast in place topping results in a slope of more than 2% at 8.33% at the head of the accessible parking space.
Once the garage is constructed, it is nearly impossible and very costly to fix noncompliant slopes at the head of accessible parking spaces. In some garages, we have been able to solve the problem by shifting the striping at accessible parking spaces. This results in the steeply sloped ground surface being located fully outside of the parking space and access aisle. The problem is that this solution is dependent upon whether the spaces can be shifted without compromising the minimum required width of the drive aisle or obstructing access to other parking spaces.
Environments for Aging: Designing Better Senior Housing
Last month, I had the opportunity to attend the Environments for Aging conference in Salt Lake City. Hundreds of professionals involved in the complex world of senior living gathered to learn from each other and to explore products and services that are designed for the senior population. It was not surprising to see the level of interest in the event; according to the US Census Bureau, 20 percent of the current US population will be 65 or older by 2029. The Baby Boomer generation, which accounts for the majority of that 20 percent, is moving into their 70s and are beginning to consider how and where they want to age. Some Boomers prefer to remain in their current homes in the communities that they helped build. Others want to move into smaller homes or prefer to transition to senior living communities. Many of these senior living communities are popping up both in suburbia and active urban centers in response to the current trend in senior housing preferences.
There are many senior housing typologies: among the most common are independent living, assisted living, and dementia care. Each type of living arrangement has specific needs that must be addressed from a design perspective.
Trends in Healthcare: Nurse Call Devices
“Trends in Healthcare” is a recurring series that focuses on exciting new designs and technologies we’re seeing in healthcare projects and provides best practices on how to ensure that these latest trends are accessible to persons with disabilities. We build on the wealth of knowledge we gain from working with healthcare design teams, construction crews, and practitioners to provide practical solutions for achieving accessible healthcare environments.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), falls account for 3 million injuries treated in emergency rooms, 800,000 hospitalizations, and 28,000 deaths each year in the U.S. One in five falls cause serious injuries such as concussions/traumatic brain injuries and hip fractures. Not only is this a public health concern, it is extremely costly. According to the CDC, medical costs directly related to injuries resulting from falls totaled more than $50 billion in 2015.[1] Within hospitals and long-term care facilities, effective implementation of interventions and design strategies to reduce patient falls are key to increased patient safety and decreased medical costs. However, it may not be possible to eliminate patient falls altogether, so features like a properly installed nurse call system can be life changing.[2]
Accessible Nurse Call Stations
Most state and local standards and regulations require nurse call devices in each public toilet room and within inpatient bath, toilet, and shower rooms.[3,4] Where provided in spaces required to be accessible, the nurse call device must also be accessible. An accessible nurse call device is one that meets the following requirements: (more…)


