- April 07, 2022
- 0 Comments
- In Accessible Design and Construction
- By Peter Stratton
The 2017 edition of the A117.1 Standard for Accessible and Usable Buildings and Facilities comes with the most significant spatial changes that we have seen in any recent code cycle. As more states and local governments adopt A117.1-2017 as the technical standard of reference under Chapter 11: Accessibility of the International Building Code, builders, developers, architects, and agencies, among others, will be faced with some big changes when it comes to accessibility requirements.
Many of the basic building block clearances that have remained relatively the same since the 1986 edition of the standard have been expanded based on the findings of The Wheeled Mobility Task Group (PDF), a study of mobility device users conducted by The Center for Inclusive Design and Environmental Access (IDeA) out of the University at Buffalo, SUNY.
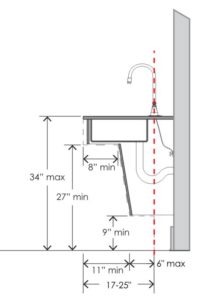
What has changed and how will designs be affected? Here are our top 5 spatial changes in A117.1-2017 and the impact those changes could have on building design: (more…)

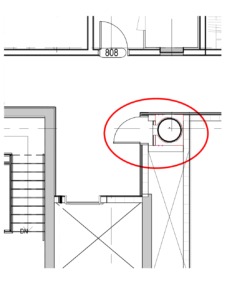 The image on the left depicts a trash chute closet (circled in red) in a
The image on the left depicts a trash chute closet (circled in red) in a