Overview
There have been several local and global developments recently with regards to off-shore wind turbines. Advancements in energy storage from both wind and solar energy, coupled with the increased rate of adoption of wind turbines could serve as a major step towards a more renewable-based energy grid and a more sustainable future.
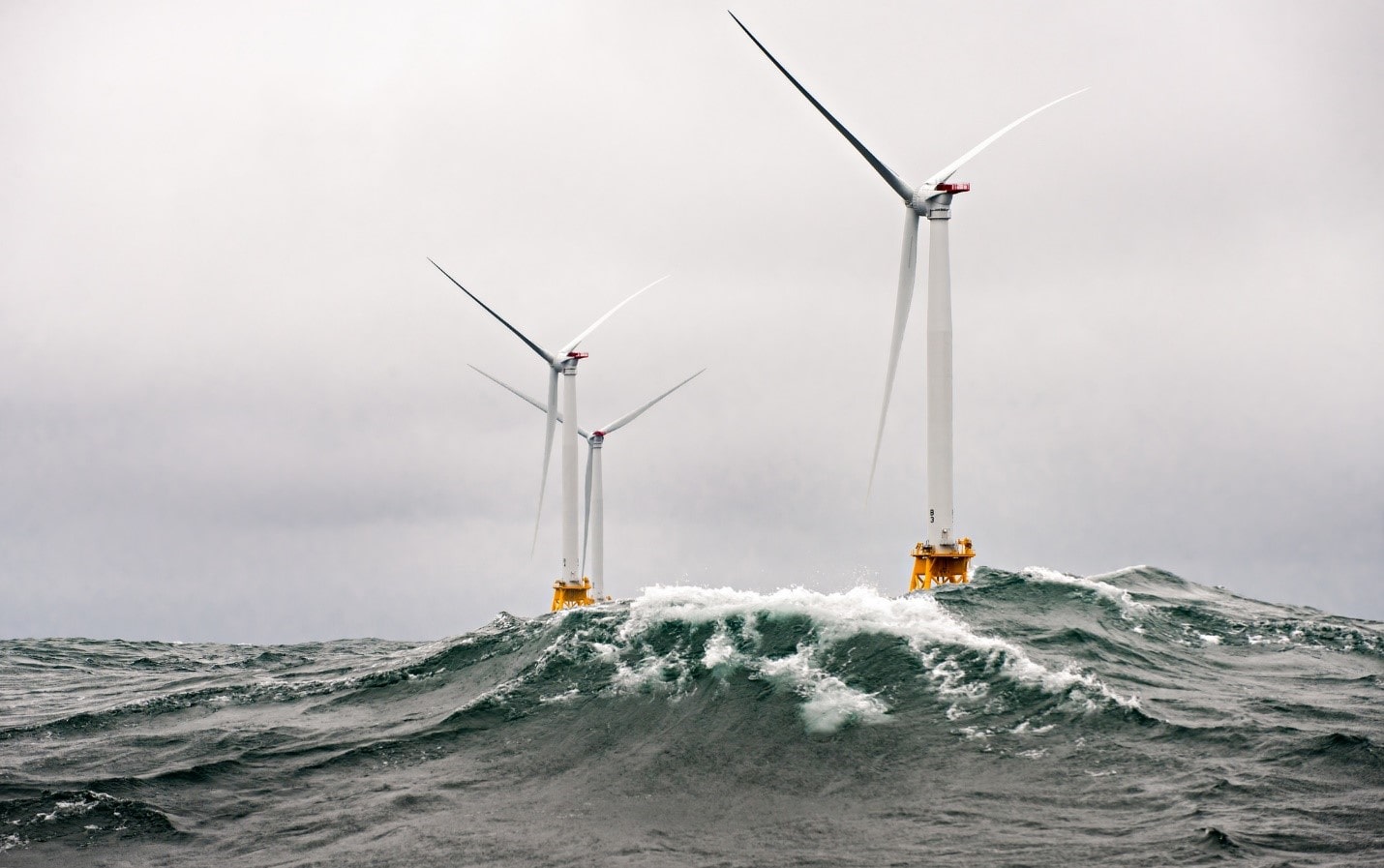

Block Island Wind Farm, courtesy of the US Department of Energy
Updates on Energy Production
First, let’s explore some recent news surrounding the adoption of off-shore wind turbines. On a global scale, Scotland’s Hywind project recently proved that technology developed for and by the oil drilling industry can be successfully applied to off-shore wind turbines.[2] The floating 30 MW wind farm, made up of five turbines off the Aberdeenshire coast, has been operational since October 2017. During a three-month period of stormy conditions from November 2018 to January 2019, the wind farm managed to continue energy production at 65% of their maximum capacity. Note that during this period, a North Atlantic hurricane produced swells up to 27 feet! Over the course of a year “maximum capacity” is approximately 135 GWh of electricity – or enough to power 20,000 Scottish homes. To ensure that the turbines can withstand weather events on that scale, the floating turbines are ballasted by 5,000 tons of iron ore, and 1,323 tons of chain anchor it to the seafloor. This off-shore farm proves that wind turbines can be successfully deployed in deeper waters where it would be increasingly expensive to extend the physical structure of the turbine tower to the seafloor. Additionally, the US, UK, Ireland, Portugal, Spain, France, and South Korea all have started to piggyback off the success of the Hywind farm in various ways. For instance, South Korea partnered with the Equinor, the primary backer of Hywind, to conduct a feasibility study for a 200 MW farm that would be located off the coast of Ulsan.[3][4][5][6]